Try Falco on Kubernetes with WebUI
Instructions to deploy a sample Kubernetes VM with Falco on it on my Windows host. I also provide a Vagrantfile which automates the process for you.
Table of Contents
Open Table of Contents
Installation
First we need to install Vagrant according to the official page.
Then we setup a basic Ubuntu VM with vagrant and ssh into it:
vagrant init bento/ubuntu-20.04
vagrant up
vagrant sshInstall helm, kubectl, and k3s:
Helm:
curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3
chmod 700 get_helm.sh
./get_helm.shKubectl:
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"k3s:
curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | sh -We need to add the Kubeconfig file to the environment variables:
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yamlInstall falco using helm
Helm is the simplest way to deploy Falco and Falcosidekick.
helm repo add falcosecurity https://falcosecurity.github.io/charts
helm repo updateCreate a namespace in which to run Falco:
kubectl create namespace falcoNow we can install falco on the cluster, make sure to enable the webui parameter:
helm install falco -n falco --set driver.kind=ebpf --set tty=true falcosecurity/falco \
--set falcosidekick.enabled=true \
--set falcosidekick.webui.enabled=trueCheck if Falco is successfully installed (all pods should be in a Running state):
kubectl get pods -n falcoRun a Test
Now that we have everything setup, we can test if Falco is working correctly. For that, we will create a basic pod and run a exec command to simulate suspicious activity:
kubectl run alpine --image alpine -- sh -c "sleep infinity"
kubectl exec -it alpine -- sh -c "uptime"We need to get the ip of our VM and port forward our WebUI service to be able to access it from our Host Machine.
ip a
kubectl port-forward svc/falco-falcosidekick-ui 2802:2802 --address 0.0.0.0 -n falcoAccess the Falco UI in your browser like this: http://<ip>:2801/
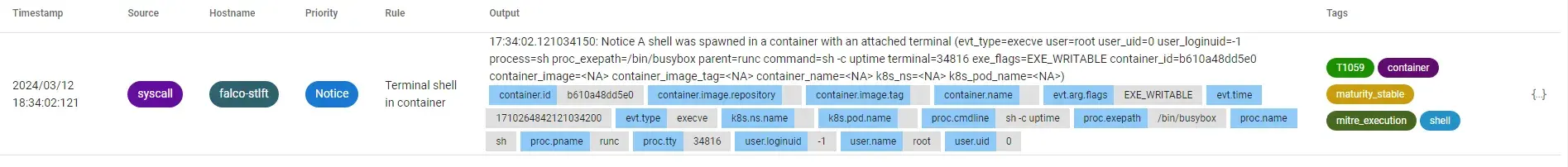
Use the default credentials admin:admin to login. We can see now under the EVENTS tab that a shell was spawned.
Vagrantfile
Here is a Vagrantfile provided which automates the process of installing Falco and its WebUI on a vm.
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.box = "bento/ubuntu-20.04"
config.vm.network "public_network"
config.vm.provision "shell", inline: <<-SHELL
apt-get update
curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3
chmod 700 get_helm.sh
./get_helm.sh
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"
curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | sh -
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml
helm repo add falcosecurity https://falcosecurity.github.io/charts
helm repo update
kubectl create namespace falco
helm install falco -n falco --set driver.kind=ebpf --set tty=true falcosecurity/falco \
--set falcosidekick.enabled=true \
--set falcosidekick.webui.enabled=true
SHELL
end